Living with diabetes involves more than just managing blood sugar levels; it also requires being mindful of potential complications, including when it comes to vision. Eye health is an essential aspect of overall well-being that can often be overlooked by diabetics. Diabetes can cause many eye diseases, including diabetic retinopathy, diabetic macular edema, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Understanding these conditions and their connection to diabetes can empower you to take proactive steps in your healthcare routine.
What Is Diabetes?
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects how your body processes glucose, the primary energy source derived from food. When you have diabetes, your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it produces. This can lead to elevated blood sugar levels, which, over time, can cause various health complications, including eye diseases.
Diabetes comes in several different types:
- Type 1 Diabetes: An autoimmune condition where the pancreas produces little to no insulin, requiring insulin injections or pumps to manage. This type generally first presents in childhood, though some adults can develop it.
- Type 2 Diabetes: A metabolic disorder where the body can produce its own insulin, but either can’t properly use it or doesn’t produce enough. About 90% of people with diabetes have type 2.
- Gestational Diabetes: A temporary condition that occurs during pregnancy, though it can increase the risk of developing diabetes later in life for both the parent and the child.
Diabetic Retinopathy
Diabetic retinopathy is an eye condition that can develop in people with diabetes, affecting the blood vessels in the retina—the part of the eye that helps us see by converting light into signals for the brain.
Initially, the condition might cause small swellings in the blood vessels. As it worsens, these vessels can become blocked, cutting off the retina’s blood supply. This can result in new, weak blood vessels growing, which might then leak or bleed, damaging the retina further. If not treated, diabetic retinopathy can lead to vision loss or even blindness. In fact, this condition is the most common type of vision loss connected to diabetes.
Symptoms of diabetic retinopathy include:
- Distorted vision
- Dark spots or strings floating in your vision (floaters)
- Blurry central vision
- Impaired colour vision
- Vision loss
While diabetic retinopathy can be managed, early detection through regular eye exams is vital as any vision loss is permanent. Treatments may include laser surgery, anti-VEGF medicine, or vitrectomy to try to prevent further damage.
Diabetic Macular Edema
The macula, located in the middle of the retina, is responsible for sharp central vision. Diabetic macular edema (DME) is a complication related to diabetic retinopathy that occurs when fluid accumulates in the macula, causing swelling. High blood sugar can weaken the small blood vessels in the eye, linking diabetes to this fluid accumulation.
Diabetes isn’t the only cause of macular edema—other causes can include age-related macular degeneration, genetic diseases, or eye surgery—but diabetes does increase your risk of developing it.
DME symptoms include:
- Distorted vision
- Washed-out colours
- Increased floaters
- Double vision
- Blurred central vision
The good news is that DME is treatable. Your eye doctor may suggest laser therapy, corticosteroid injections, or anti-VEGF injections to reduce fluid build-up and restore vision clarity.
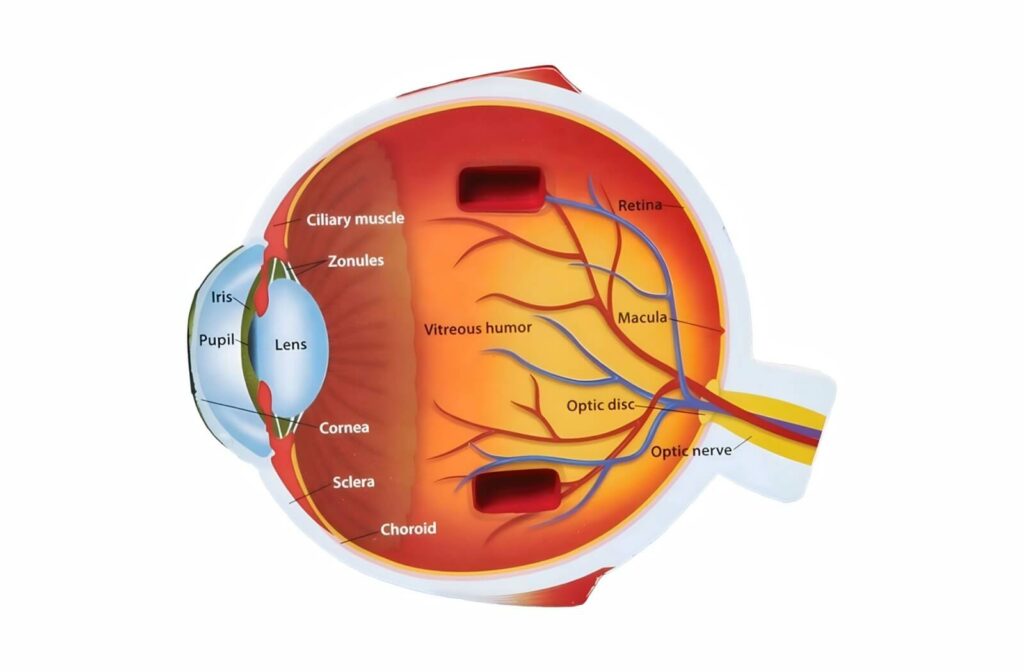
Cataracts
Cataracts develop when the eye’s lens becomes cloudy, leading to hazy vision. Cataracts are a natural part of aging that most people will develop at some point in their lives, but those with diabetes are more likely to develop cataracts at an earlier age. This happens because high blood sugar levels can cause changes in the lens’ structure, leading to cataract formation.
Symptoms of cataracts include:
- Cloudy or blurred vision
- Difficulty seeing at night
- Double vision
- Halos around lights
- Light sensitivity
- Poor night vision
- Fading or yellowing of colours
Cataracts are easily treatable and cataract surgery is one of the most common surgical procedures performed in Canada. This low-risk procedure involves removing the cloudy lens and implanting a clear artificial lens.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma refers to a group of diseases that damage the optic nerve, often due to elevated eye pressure, leading to vision loss. Diabetes can double your risk of developing open-angle glaucoma, the most common glaucoma type.
Glaucoma often has no early symptoms. You may only realize you have it after losing some of your vision, typically starting with your peripheral vision. An optometrist can test for glaucoma during an eye exam and start treatment to lower your intraocular pressure.
Tips for Managing Diabetes
A lot of the damage diabetes can cause is irreversible, so make sure to focus on proactive care. Managing diabetes effectively is key to protecting your eye health. Type 1 diabetes requires insulin, but it’s possible to manage type 2 diabetes with lifestyle changes. Always listen to your doctor’s advice, and consider some of the following tips:
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to help regulate blood sugar levels and reduce blood pressure.
- Monitor your blood sugar levels as advised by your healthcare provider.
- Attend regular check-ups with your healthcare team.
- Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Protect Your Vision & Prioritize Eye Health
Your eyes are precious, and taking care of them is crucial, especially if you’re living with diabetes. Regular eye exams can make a world of difference in detecting and managing eye diseases early. At Eye on Evanston, we’re committed to helping you safeguard your vision with comprehensive eye care services.
Our knowledgeable optometrists are ready to provide personalized care in a warm and welcoming environment. Book an appointment with us today and take the first step toward preserving your eye health.
We can’t wait to see you!